The Human Mouth
The human mouth is a complex structure that consists of both hard and soft tissues forming a hollow cavity. The mouth anatomy features several components including the jaws, teeth, gums, tongue, palate, cheeks, lips, which all together contribute in making possible the various functions of the mouth. The mouth is also referred as oral cavity or buccal cavity.
The main parts of Human Mouth Anatomy
The mouth provides the opening through which food and air can enter the human body. Its anatomic boundaries are defined by the lips at the front, the cheeks at the sides, the tongue and floor of mouth at the bottom, the palate at the top, and the oropharynx at the back.
The different parts of the mouth play an important role in our daily lives. They work together to chew, grind and swallow foods, distinguish tastes, speak, and express our emotions.
The main parts of the mouth anatomy include the following:
- The Lips are the soft parts of tissue that form the anterior boundary of the mouth. They can seal the oral cavity and contribute in several behavioral expressions such as kissing or laughing.
- The Cheeks form the sidewalls of the mouth.
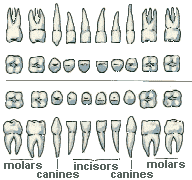
- The Teeth are the white colored calcified structures within the lower and upper jaws, which we use for chewing.
- Periodontium is a group of supporting tissues that surround teeth and keep them in place.
- The Gingiva (Gums) is the pink soft tissue that surrounds teeth and covers the jaw bone.
- The Periodontal Ligament is a layer of connective tissue fibers which hold the tooth anchored inside the alveolar socket of the jaw.
- Alveolar process is the part of alveolar bone around the tooth sockets where teeth roots are anchored.
- The Tongue is a muscular organ that helps us taste foods, chew and swallow them. It contains a large number of ‘taste buds’ that can sense the 4 main tastes: sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
- Jaws are the two bony structures that form the skeleton of the mouth and carry the 32 human teeth.
- The upper jaw, called ‘maxilla’, is fixed with the skull and holds the top row of teeth.
- The lower jaw also known as mandible is the largest, strongest and the only movable bone of the face. Its ability to move almost in all directions is important for our ability to chew properly.
- Temporomandibular Joint is the joint that connects the lower jaw (mandible) with the skull.
- The Palate is the roof of the mouth, separating it from the nasal cavity. It is divided into hard and soft palate.
- The Salivary Glands provide our mouth with saliva. There are 3 pairs of major salivary glands, and hundreds of smaller ones around the mouth. Saliva is a biological fluid that moistens and protects the mouth, starts break down foods with its enzymes, and facilitates swallowing.
- The Floor of the Mouth is formed mostly by the tongue and by mucous membranes that extend from the base of the tongue to the gums of the lower jawbone.
- The Muscles of the mouth help us perform the controlled movements of the various parts of the mouth (jaw, lips, tongue, cheeks) so that we can eat, speak and express ourselves.

