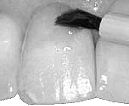
Fluoride Varnish
Fluoride varnish provides the most effective way of topical fluoride application on a child’s teeth. Fluoride varnishes prevent and even reverse early childhood caries. They have proven efficacy in reducing cavities in both primary and permanent teeth.
A fluoride varnish is a professionally applied adherent material which consists of high concentration of fluoride in fast drying, alcohol based solutions of natural varnishes. Fluoride varnishes were first developed in Europe in 1960.
Fluoride varnishes were first used as a treatment for sensitive teeth problems, but dentists soon realised their high potential in anti-caries prevention and especially against early childhood caries.
Efficacy of topical fluoride varnishes
Clinical studies have demonstrated that varnishes can supply fluoride on tooth surfaces more efficiently than other topical agents like the fluoride solutions and gels. Results have shown from 25% up to 75% caries reduction resulting from fluoride varnish use. Varnishes need to be re-applied at regular intervals to maintain their efficacy (every 6 months).
Topical fluoride varnish application
Because of the high concentration of fluoride (up to 20 times higher compared to a toothpaste) fluoride varnishes are available only to dental professionals. Topical fluoride varnish application is recommended for infants and childen with moderate or high risk of developing caries, if there is need for additional fluoride supplementation.
Application is quick and easy. Fluoride varnish is painted directly to the tooth surface (on to enamel or cementum). Its purpose is to hold fluoride in closed contact with the tooth for a period of time. It hardens into a clear or yellowish film coating in the presence of saliva.
The child should not brush the evening following the fluoride varnish application, but should resume normal brushing routine the following morning.
Mechanism of action of topical fluoride varnishes
Fluoride is used to help prevent tooth decay. It works by strengthening the mineral composition of the tooth enamel, which makes the teeth more resistant to acid attacks by dental plaque bacteria in the mouth. All currently used topical fluoride agents deposit soluble fluoride as calcium fluoride on enamel. Calcium fluoride serves as a source of fluoride for the formation of fluorapatite
Fluoride varnish painted on to enamel or cementum hardens to a clear or slightly yellowish film. It acts by a slow release of fluoride to the underlying tooth surface. Increased fluoride ion concentration that results after fluoride varnish, actually enhances mineral deposition, reduces the rate of demineralization and promotes remineralisation. The greater fluoride concentrations attainable with varnishes produce deposits of calcium fluoride in the porous structure of the enamel. These reservoirs gradually release fluoride into dental plaque, saliva and tooth structure when the pH drops.
Advantages of fluoride varnish versus traditional fluoride gels, foams etc
- Fluoride varnish acts in two ways :
1. quickly adheres to teeth promoting tooth remineralization, and
2. it is also slowly released to the tooth surface over time, providing on-going fluoride protection, enhancing its effectiveness versus the rest of the topical fluoride treatments. - Quick and easy to apply. Applying the varnish takes less than two minutes, making it ideal for patients who are anxious or who have special needs
- It is safer to use. The amount of fluoride swallowed is small or negligible, which makes it acceptable for use in very young children.
- Tastes better, compared to fluoride gels, making it more acceptable by infants. Fluoride varnish is available in various flavors.
- Does not require the use of trays that may trigger gag reflex.
- Does not require the use of sophisticated dental equipment and instruments.
Safety issues of fluoride varnishes
Fluoride varnish has a higher concentration of fluoride than gels, foams, rinses and pastes, but the amounts of fluoride exposure can be better controlled because less of it is swallowed during application.
Studies have shown that fluoride absorption is lower among fluoride varnish users than users of other topical treatments, reducing the risks of fluoride side effects such as fluorosis. Dental fluorosis is a condition that occurs when children ingest too much fluoride during the period of enamel formation.
Daily oral hygiene is essential for maintaining oral health. It should also be combined with proper healthy diet and regular dental visits.


